总览汇总
| 文章题目 | 本地文件位置 | 年份 | 发表刊物 | 解决问题 | 方法 | 关键创新点 | 数据集 | 代码 | 实现难易程度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scalable Gradients for Stochastic Differential Equations | duval23a.pdf | 2023 | JMLR | 1. 通过Stochastic Frame Averaging变换保留原子坐标的投影对称性,数据处理值得借鉴。 2. 然后结合GNN和MLP构建了神经网络,这部分并未很突出。 3. 取得较好的表现。 |
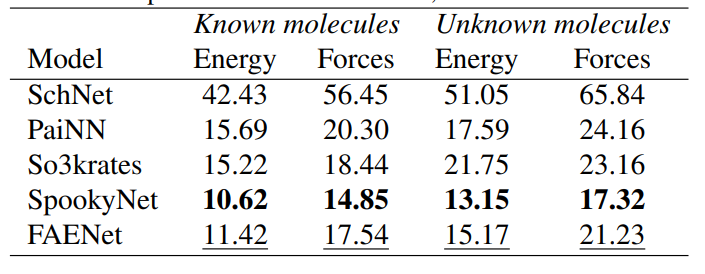
Stochastic Frame Averaging: PCA降维 | 对称保持的数据增强:研究者提出了一种新方法,使得GNN在处理数据时可以保持其原始的对称性。 FAENet:这是研究者开发的一个新的GNN模型。它的特点是可以自由地处理原子之间的位置关系,同时确保数据的对称性不被破坏。 FAENet分析:研究者测试了他们的新方法和新模型在几个材料科学数据集上的性能,并发现它比以前的方法更好。 | OC20 dataset (S2EF, IS2RE),(QM9, QM7-X) | 1.FAENet: Frame Averaging Equivariant GNN for Materials modeling — faenet documentation 2. vict0rsch/faenet (github.com) | 使用较为容易,修改需要熟悉代码, 估计熟悉代码需要两周。 |
| Flashlight: Scalable Link Prediction With Effective Decoders | wang22d.pdf | 2022 | PMLR | 比较远的原子在多路信息传递的信息丢失和区分键角不同的结构。 | 1. frame construction 2. coordination projection 3.frame-frame projection | even ordinary GNN can encode molecule injectively and thus reach maximum expressivity with coordinate projection and frame-frame projection. | MD17 | GraphPKU/GNN-LF (github.com) | 代码结果较为简单,估计一周可以熟悉并复现。 |
| Deep Potential Molecular Dynamics: a scalable model with the accuracy of quantum mechanics End-to-end Symmetry Preserving Inter-atomic Potential Energy Model for Finite and Extended Systems |
NeurIPS | 2017/2018 | PRL/NeurIPS | Molecular modeling, Inter-atomic potential energy surface modeling | Deep Potential - Smooth Edition (DeepPot-SE) | Extensive, continuously differentiable, linear scalability, symmetry preservation | 各种系统,包括高熵合金(基于DFT数据, 阿里云数据已过期) | DeePMD-kit (github.com) | 基于TensorFlow实现,使用较为方便,对其进行修改比较困难,不太熟悉TensorFlow框架。 |
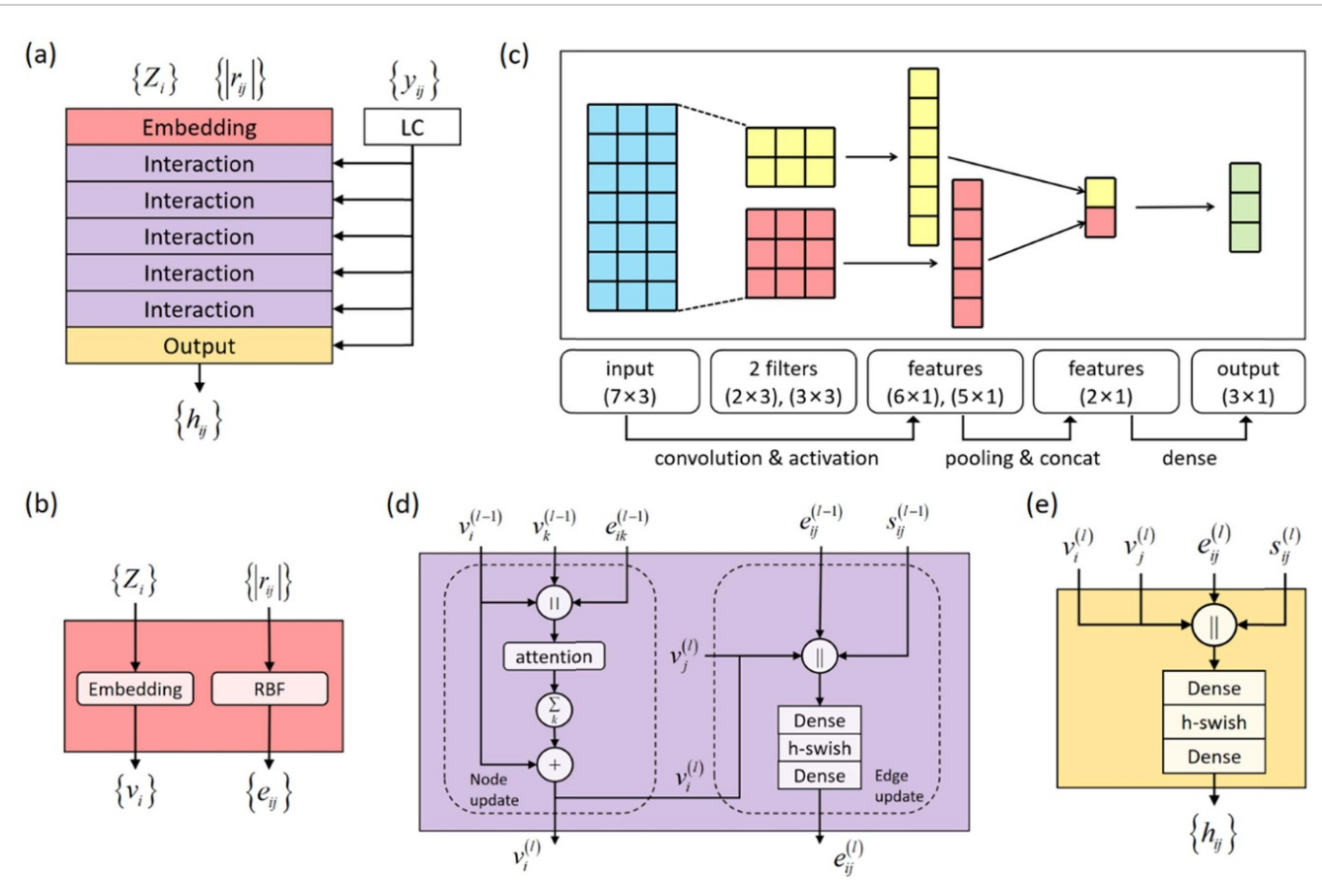
| Efficient determination of the Hamiltonian and electronic properties using graph neural network with complete local coordinates | Su_2023_ | 2023 | MLST(machine learning: Science and Technology) | 使用图神经网络(Graph Neural Network, GNN)架构和LC变换(LC transformation)构建原子体系与哈密顿量(由下面的hopping parameter给出)的关系,$h_{i \alpha, j \beta}^{\left(\mathbf{R}n\right)}=\left\langle\phi{i \alpha}\left(\mathbf{r}-\boldsymbol{\tau}_i\right) | \hat{H} | \phi_{j \beta}\left(\mathbf{r}-\boldsymbol{\tau}_j-\mathbf{R}_n\right)\right\rangle$ | LC变换(LC transformation), GNN | 使用哈密顿量作为回归的lable。 |
Self Made dataset:Graphene and , zincblend SiGe |
| Cormorant:协变分子神经网络 | PDF链接 | 2019 | NeurIPS | 开发名为Cormorant的神经网络架构,专为学习复杂多体物理系统的行为和性质。 2. 应用于分子系统,学习用于分子动力学模拟的原子势能面及由密度泛函理论计算的分子基态特性。 3. 确保网络的旋转不变性,增加网络的表达力。 | 输入特征化网络,只对原子电荷/身份和相对位置的标量函数进行操作。 2. 协变激活网络,每个激活都是$\mathrm{SO(3)}$-向量类型。 3. 顶部的旋转不变网络,从激活构造标量,用于预测回归目标。 | Clebsch-Gordan非线性,实现激活中每个自由度的完全交互。 2. 确保网络的旋转和平移不变性,神经元实现的操作直接由已知的物理相互作用的形式激发。 3. 网络激活以球形张量形式(SO(3)–向量)表示,结合Clebsch–Gordan乘积和可学习权重的混合,所有操作都是协变操作。 | MD-17数据集(学习分子力场和势能表面), QM-9数据集(学习一组分子的基态性质, 前文使用的数据) | github链接: | 重现代码较为容易,代码实现设计较为复杂的物理数学原理,修改可能比较困难。 |
| Do Transformers Really Perform Bad for Graph Representation? | 探讨Transformer在图表示学习中的表现,并提出Graphormer来提升性能 | NeurIPS | Graphormer的提出,通过结构编码方法来优化Transformer对图结构数据的处理。 | . 中心性编码:使用度中心性来为每个节点分配嵌入向量。 2. 空间编码:衡量节点间的最短路径距离,将其作为偏置项加到注意力矩阵中。 3. 边编码:计算边特征与可学习嵌入的点积的平均值,作为偏置项加到注意力模块中。 | OGB Large-Scale Challenge (OGB-LSC) 中的 MAG240M, WikiKG90M, PCQM4M数据集 2. OGBG-MolPCBA, OGBG-MolHIV, ZINC(sub-set) | Graphormer on GitHub | 具有较为完备的代码和教程,复现不困难,进行修改难度需要进一步评估。 | ||
| E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials | 链接 | 2022 | Nature Communications | 1. 加速分子动力学模拟的深度学习原子势方法的引入。2. 提高了分子和材料集合的准确性,同时展现了显著的数据效率。 | **Neural Equivariant Interatomic Potentials (NequIP)**:E(3)-equivariant neural network 方法用于从ab-initio计算中学习分子动力学模拟的原子势。 | E(3)-equivariant卷积:与大多数仅在标量上作用的当前对称感知模型不同,NequIP采用E(3)-equivariant卷积来处理几何张量的交互,从而更丰富、更真实地表示原子环境。 | 1. MD-17 Dataset 2. QM9 Dataset 3. ISO17 Dataset | http://github.com/mir-group/nequip | 有较为完备的文档和项目以及实现,上手起来应该比较容易。 |
数据集汇总
OC20 Dataset (S2EF, IS2RE):
- The Open Catalyst 2020 Dataset (OC20) is used for catalysis in chemical engineering, with a focus on molecules significant in renewable energy applications. It includes over 1.3 million relaxations of molecular adsorptions onto surfaces, making it a substantial dataset for electrocatalyst structures.
- The dataset provides Bader charge data for all final frames in its training and validation systems. It’s organized in a .tar.gz file, which, when uncompressed, reveals several directories with unique system IDs. Each directory contains raw Bader charge analysis outputs (source).
- Data in OC20 is stored in PyTorch Geometric Data objects and saved in LMDB files, including several sized training splits for different tasks (source).
- It comprises 1,281,121 Density Functional Theory (DFT) relaxations across various materials, surfaces, and adsorbates (nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen chemistries) (source).
QM9 Dataset:
- QM9 provides quantum chemical properties for a relevant, consistent, and comprehensive chemical space of small organic molecules. It’s become a standard for machine learning predictions of various chemical properties.
- The dataset consists of about 130,000 molecules with 19 regression targets. Each molecule includes complete spatial information for the single low energy conformation of the atoms in the molecule (source).
- It contains 133,885 stable small organic molecules made up of CHONF (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine) and is publicly available for data-driven researches of material property prediction and chemical space exploration (source).
QM7-X Dataset:
- QM7-X is a comprehensive dataset with approximately 4.2 million equilibrium and non-equilibrium structures of small organic molecules. It provides 42 physicochemical properties for these molecules, which comprise up to seven non-hydrogen atoms (C, N, O, S, Cl).
- The dataset is organized into HDF5 files, and a script is provided to produce a database file named QM7X.db containing atomic position, atomic number, and the required physicochemical properties (source).
- It covers a broad range of physicochemical properties, making it a valuable resource for researchers interested in the quantum-mechanical properties of small organic molecules (source).
MD17 Dataset:
The MD17 (Molecular Dynamics 17) Dataset was introduced by Chmiela et al., focusing on energies and forces for molecular dynamics trajectories of eight small organic molecules.
The dataset has been used for the development and evaluation of machine-learned potential energy surfaces (PES). Each molecule in the database comprises tens of thousands of energies and forces obtained from DFT (Density Functional Theory) direct dynamics at 500 K. Notable examples of molecules included are ethanol, malonaldehyde, and glycine (source). -
A revised version of the dataset, known as rMD17, was introduced by Anders S. Christensen and O. Anatole von Lilienfeld in 2020. This version recalculated the energies and forces at a different level of theory, aiming to address the role of gradients in machine learning of molecular energies and forces. Moreover, a third version of the dataset was introduced, containing fewer molecules computed at the CCSD (T) (Coupled Cluster with Single and Double excitations) level of theory (source).
The original MD17 dataset contained numerical noise, which was noted and addressed in the revised version to ensure accuracy in machine learning benchmarks (source).
- Self Made dataset: Graphene and , zincblend SiGe:
Graphene :
We perform molecular dynamics simulation of a 6 × 6 × 1 graphene structure for 5 ps to generate the dataset. sample 500 structures as the training set and the other 500 structures as the validation set
zincblend SiGe:
The SiGe random alloy dataset is generated by randomly occupying the zinc-blende lattice sites with the Si or Ge atoms. The number of possible combinations in a supercell with N sites is given by the combinatorial number C(N,N/2), which could be incredibly large as the total atom number increases.
ISO17 Dataset:
Description: The ISO17 dataset, also known as “ISO17 - MD Trajectories of C7O2H10 with total energies and atomic forces,” is derived from a set of molecules from the QM9 dataset with a fixed composition of atoms (C7O2H10) in various chemically valid structures. These molecules were selected from the largest set of isomers in the QM9 dataset[^1^].
Composition: The dataset contains:
X(7165 x 23 x 23): Inputs (Coulomb matrices)T(7165): Labels (atomization energies)P(5 x 1433): Splits for cross-validation[^2^]Benchmark for Molecular Dynamics: ISO17 is a benchmark dataset for molecular dynamics of C7O2H10 isomers, including molecular forces[^3^].
Extension of Isomer MD Data: The dataset is an extension of the isomer MD data used in prior research[^4^].
References and Further Reading: - Quantum-Machine.org: Datasets - SchNetPack Documentation - kgcnn Documentation
术语说明
- $ E(3) 3-dimensional Euclidean group,$
指的是欧几里得空间中的刚体变换(或称为欧几里得变换)。这种变换在三维空间中保持距离和角度不变。具体来说,( E(3) ) 变换由以下两部分组成:
旋转:这是一个保持原点不变的变换,它可以使物体绕某个轴旋转。
平移:这是一个将物体从一个位置移动到另一个位置的变换,而不改变物体的方向或形状。
This includes translations, rotations, and reflections. An E(3)-equivariant neural network is designed to respect these symmetries, meaning that its output will change appropriately with such transformations of the input data.
- $PES$
输入原子坐标,得到能量和受力的任务。
- Equivariance
For Equivariance in neural neural network, that means the output of the neural network can be predicted when the input data is transformed, or to say the output is also given in the same transformed way as the input day or in a correlation way.
具体论文
FAENET
论文阅读报告
论文标题
FAENet: Frame Averaging Equivariant GNN for Materials Modeling
主要贡献与目标
- 目标:提高材料属性预测模型的计算效率和预测能力。
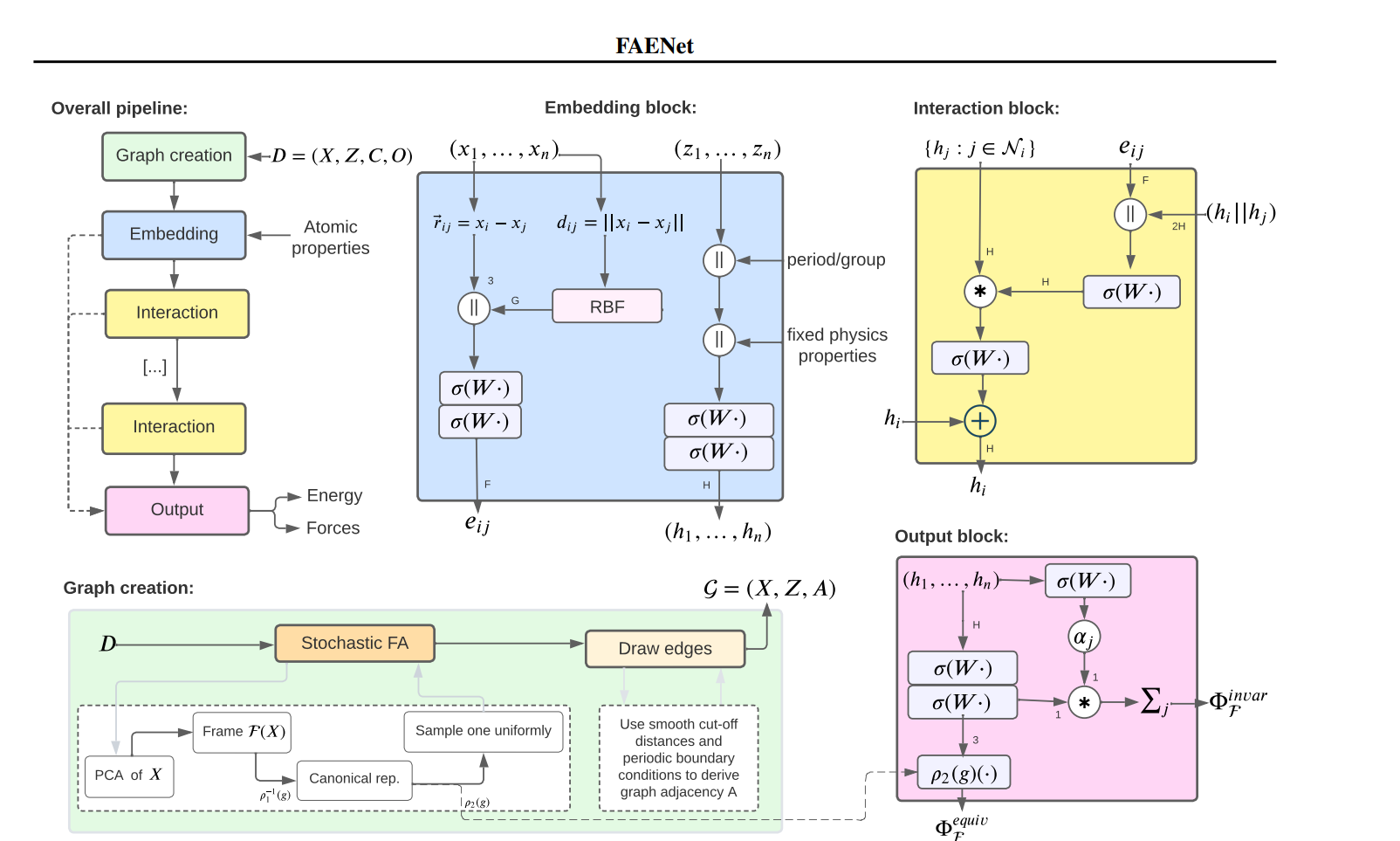
- 方法:引入了一种新的框架和网络,即Stochastic Frame-Averaging (SFA)和FAENet,以在不丧失表达能力的情况下实现E(3)-等变性。
- 应用:这些方法适用于广泛的分子属性预测,并在OC20、S2EF、IS2RE、QM9和QM7-X等数据集上进行了实证验证。
关键方法与技术
- **Stochastic Frame-Averaging (SFA)**:一种灵活的框架,通过将数据点投影到规范表示中,允许任何模型在理论上(Full FA)或经验上(Stochastic FA)实现E(3)-等变性,而不失去表达能力。
- FAENet:一种轻量级但有效的GNN,其设计不受对称性保护要求的约束。FAENet可以通过原子相对位置处理几何信息,同时通过数据严格保持对称性,由FA提供支持。
主要挑战与问题
- 现有的基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的模型在计算上非常密集,限制了大量材料候选项的评估。
- 以前的方法在实现表达性和泛化能力的同时,可能在训练和推理方面计算成本很高。
方法论证与分析
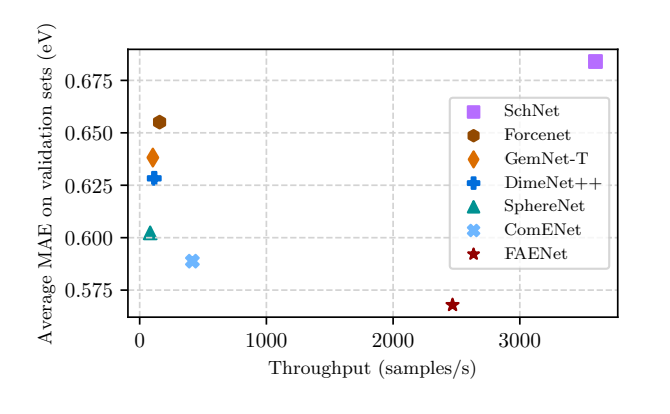
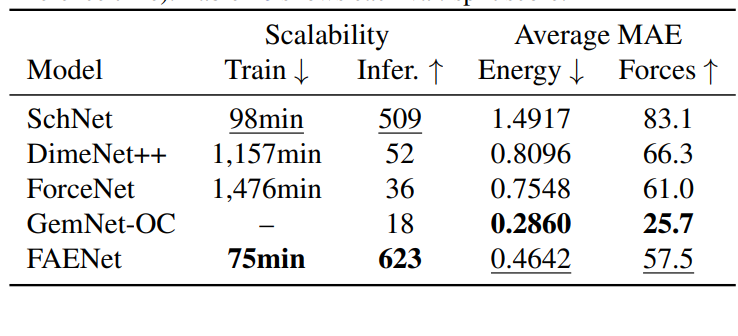
- 理论验证:验证了所提出方法的理论属性,研究了其表达能力,并在四个众所周知的材料科学ML数据集上展示了其与先前方法相比在精度和可扩展性方面的优越权衡。
- 实证分析:在OC20 IS2RE、S2EF(2M)用于固态晶体结构建模,以及QM7-X和QM9用于分子建模的数据集上展示了其优越的精度与可扩展性权衡。
相关工作
- 数据增强:以前的工作使用数据增强来在不约束模型架构的情况下合并所需的数据对称性,但精度与可扩展性的收益不足以构成真正的帕累托最优改进。
- 等变方法:先前的方法专注于通过使用SO(3)群的不可约表示来强制实施等变性。虽然这些方法表达性强且泛化能力强,但在训练和推理方面可能非常计算密集。
结论
该论文通过引入SFA和FAENet,提出了一种新的视角和方法,以数据投影的方式保持对称性,而不是通过架构约束。这些方法旨在创建表达能力强、健壮且计算上可扩展的模型,以便进行大规模的材料属性评估和预测。在多个数据集上的实证验证表明,这些方法在精度和计算可扩展性方面提供了优越的权衡。
GNN-LF
论文阅读报告
论文标题
Graph Neural Network with Local Frame for Molecular Potential Energy Surface
主要贡献与目标
- 目标:高效且准确地模拟分子势能面(PES)。
- 方法:引入一种新的局部帧方法来学习分子表示,并分析其表达能力。通过在一个框架上投影,将等变特征(如3D坐标)转换为不变特征,从而在不复杂化架构的情况下捕获几何信息,并从GNN设计中解耦对称性要求。
- 结果:尽管使用了一个简单的普通GNN架构,但模型实现了最先进的准确性,并且具有更高的可扩展性,与最高效的基线相比,仅需要大约30%的推理时间和10%的GPU内存。
方法论证与分析
- GNN-LF模型:该模型为每个原子生成一个O(3)-等变框架,并将邻近原子的相对位置和框架投影到该框架上作为边特征。这允许一个普通的GNN在只有不变特征的图上工作,确保表达能力和更简单的架构。
- 局部帧:局部帧方法解耦了对称性要求,允许模型在不变表示空间中操作,必要时可以将其转换回等变预测。
- 表达性:作者证明,给定非退化帧,即使是普通的GNN也可以通过坐标投影和帧-帧投影注入地编码分子并达到最大的表达性。
挑战与问题
- 现有的GNN需要特殊的设计来捕获几何信息并满足对称性要求,导致架构复杂。
- 手动描述符模型由于硬编码的描述符而准确度较低,不能处理可变大小的分子或不同种类的原子。
- 现有的GNN模型在如何合并几何信息方面存在差异。一些使用仅旋转不变的几何特征,而其他一些利用与坐标变换变化的等变特征。
结论
该论文通过引入GNN和局部帧方法,提出了一种新的方法来模拟分子PES,允许捕获几何信息并从GNN设计中解耦对称性要求。所提出的模型,GNN-LF,使用简单的GNN架构,但实现了最先进的准确性,并提供了与高效基线相比更高的可扩展性。作者通过实验提供了理论证明和方法的优越性能和可扩展性的演示。
LC-NET